Acceleration Card
| Introduction |
|---|
R80.20 and above offer many technical innovations regarding R77 and R80.10. I will look at the new Falcon Acceleration Cards in this article.
SecureXL is a software acceleration product installed on security gateways and new acceleration cards. Performance Pack uses SecureXL technology and other innovative network acceleration techniques to deliver wire-speed performance for security gateways. SecureXL is implemented either in software or in hardware:
- SAM cards on Check Point 21000 appliances
- ADP cards on IP Series appliances
- Falcon cards (new in R80.20) on different appliances
The SecureXL device minimizes the connections that are processed by the INSPECT driver.
| New acceleration Falcon architecture |
|---|
The new acceleration Falcon architecture with R80.20+:
- Low Latency
- High Connections Rate
- SSL Boost
- Deep Inspection Acceleration
- Modular Connectivity
- Multible Acceleration modules
- Falcon 1G (8×1 GbE), 10G (4×10 GbE) and 40G (2×40 GbE)
- Compatible with 5900, 15000 & 23000 Appliance Series
What’s new in acceleration high level architecture:
- SecureXL on Acceleration Card (AC)
- Streaming over SecureXL
- Lite Parsers
- Async SecureXL
- Scalable SecureXL
- Acceleration stickiness
- Policy push acceleration
| SecureXL architecture on Acceleration Card |
|---|
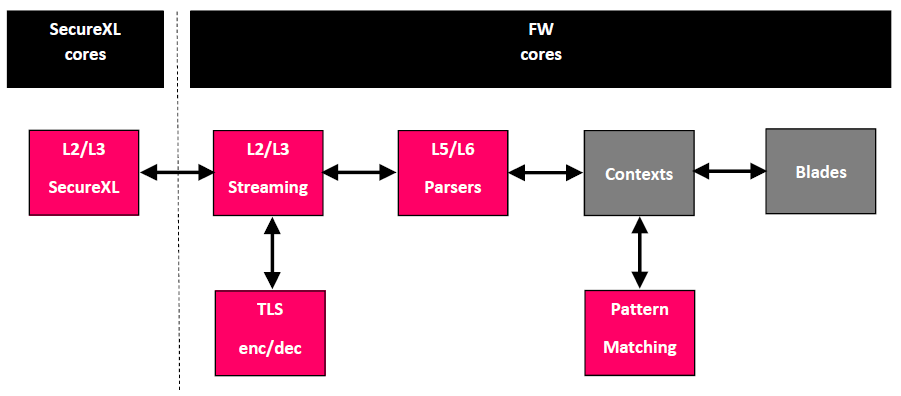
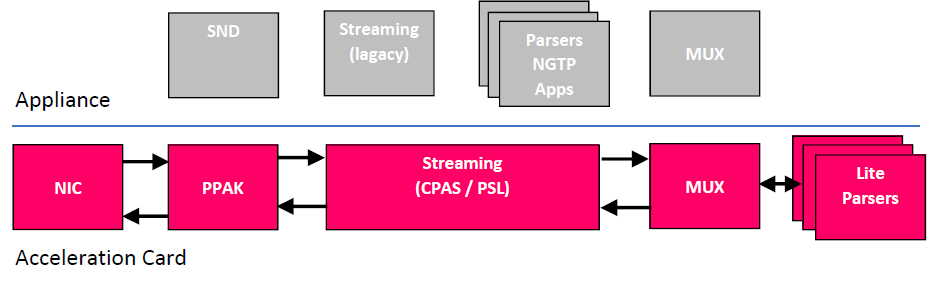
R80.20 SecureXL adds support for Falcon cards to offloading from appliance to acceleration card leaving the appliance to do more.
Following features are offloaded to the acceleration card:
- SecureXL
- Streaming
- TLS encryption und decryption
- Parsers
- Pattern Matching
Following features are working on the host (appliance):
- Contexts
- Blades (incl. user space)
- Rule base
- Headers
- And more complex logic
The following flowchart shows the new offloaded features of falcon architecture in pink.
Streaming – serves an important function in the NGTP software architecture. The streaming process creates an ordered packet stream and directly performs a number of security functions on the stream. NGTP can assemble packets into a stream in two ways, passive or active, depending on the nature of the traffic. Each has advantages and disadvantages. The passive mode (PSL) gives little opportunity for modifying the traffic stream. In contrast, the active mode can modify the connection. Active mode essentially proxies the TCP connection and is necessary when performing HTTPS inspection. Active streaming (CPAS) also facilitates timing and buffering when inspecting content such as large files. Keeping the goals of integrated, high security effectiveness and performance in mind, Check Point chose to provide the option to do passive and active streaming, which provides the best balance of security and optimized performance based on actual usage conditions.
Pattern Matcher – Security modules each have a distinct function and they register with the CMI to receive particular context types.
Parsers – Protocols include HTTP, SMTP, DNS, IMAP, Citrix, and many others. Protocol parser instances register with the streaming engine in order to receive ordered streams of data, both client-to-server (C2S) as well as server-to-client (S2C) streams.
TLS encoder/decoder – encrypt and decrypt TLS sessions.
| Acceleration Card Path |
|---|
R80.20 acceleration cards provide three new acceleration flows:
- Host path
- Buffer path
- Inline path
Host Path – For non acceleration connections (eg. local connections) and connections on non acceleration card interface.
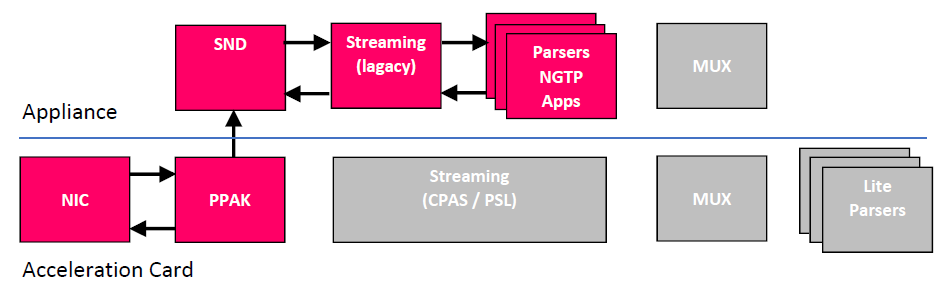
Buffer path – For HTTP requests, HTTP response headers and TLS handshakes.
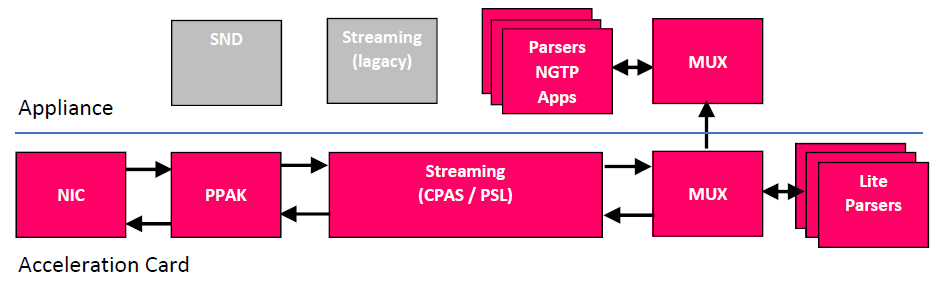
Inline path – For HTTP response body (until 1st tier match) and TLS bulk encryption/ decryption.
| References |
|---|
R&D meeting Israel
Copyright by Heiko Ankenbrand 1994-2019
